Stored XSS Vulnerability in Emlog Pro via HTML Injection
Stored XSS Vulnerability in Emlog Pro via HTML Injection
Vulnerability Description
A stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability has been discovered in Emlog Pro 2.5.19. The vulnerability exists in the email template configuration component located at /admin/setting.php?action=mail, which allows administrators to input HTML code that is not properly sanitized, leading to persistent JavaScript execution.
Affected Product
- Product: Emlog Pro
- Version: 2.5.19
- Component: Email Template Configuration (
/admin/setting.php?action=mail) - CWE: CWE-79: Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’)
Technical Details
I deployed the latest version of Emlog Pro 2.5.19 locally using PHPStudy. The source code is available at: https://www.emlog.net/download
During security analysis of the administrative interface, I discovered that the email template configuration page allows direct HTML input without proper sanitization or validation. This creates an entry point for stored XSS attacks.
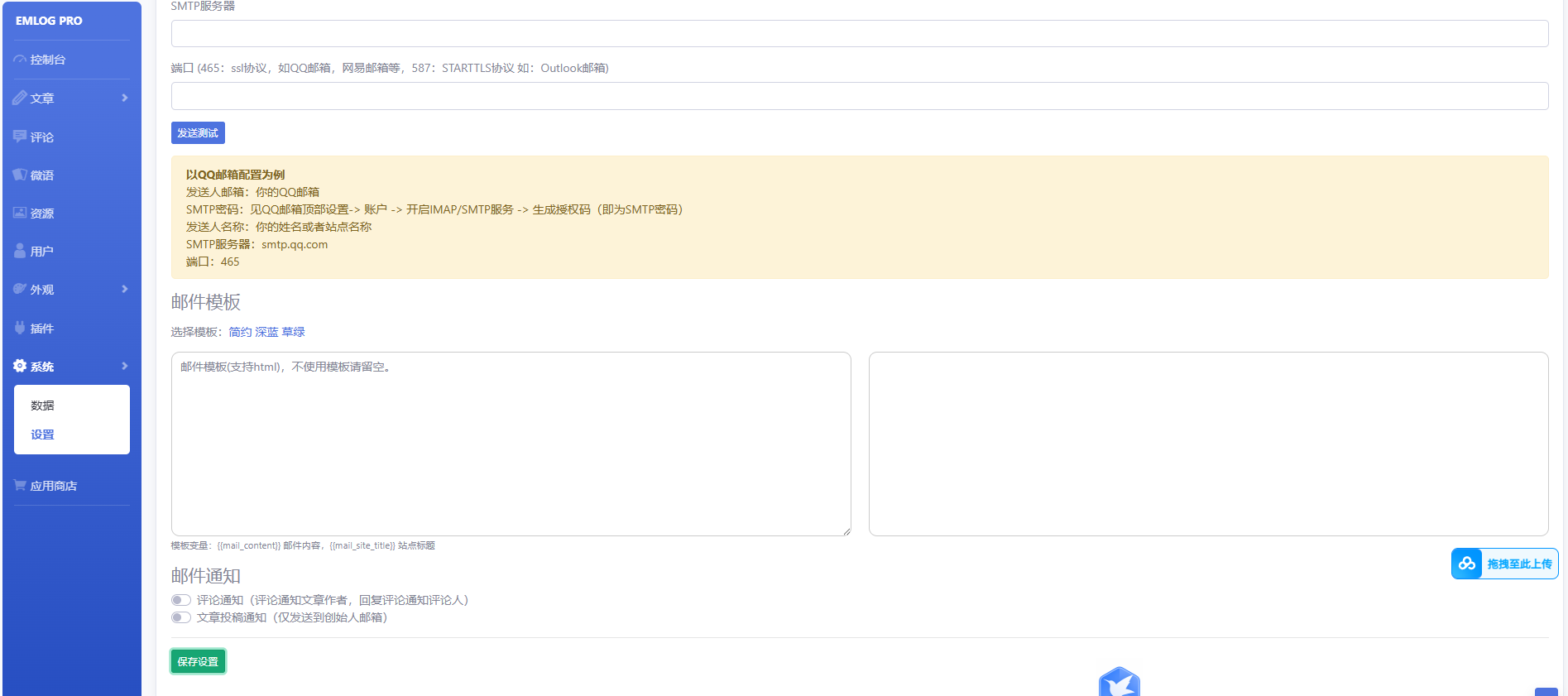
Proof of Concept (PoC)
After identifying the vulnerability in the email template component, I injected the following malicious HTML code:
1 | |
Upon insertion of this code, the JavaScript is immediately executed in the browser:
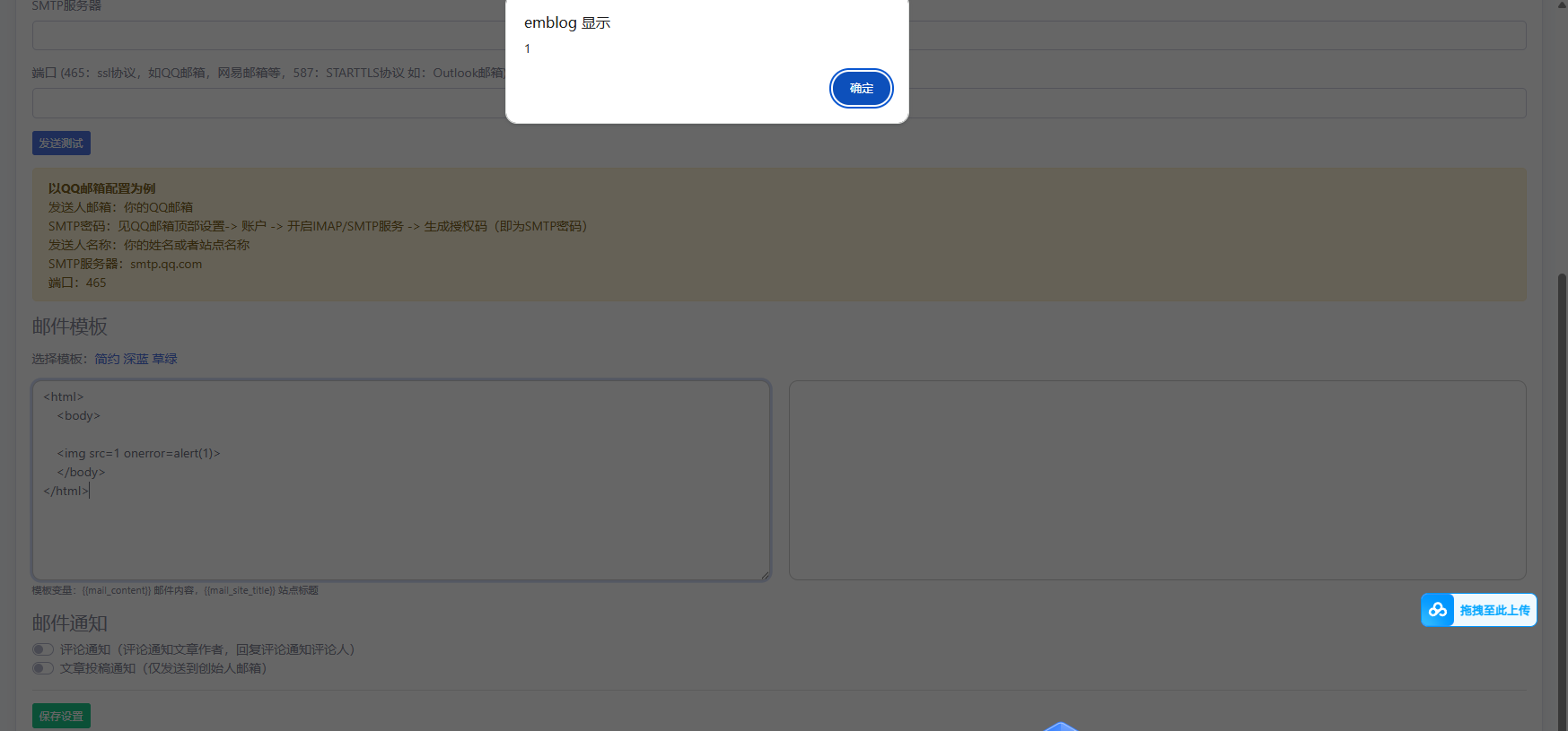
After saving the settings, the malicious code is stored in the database:
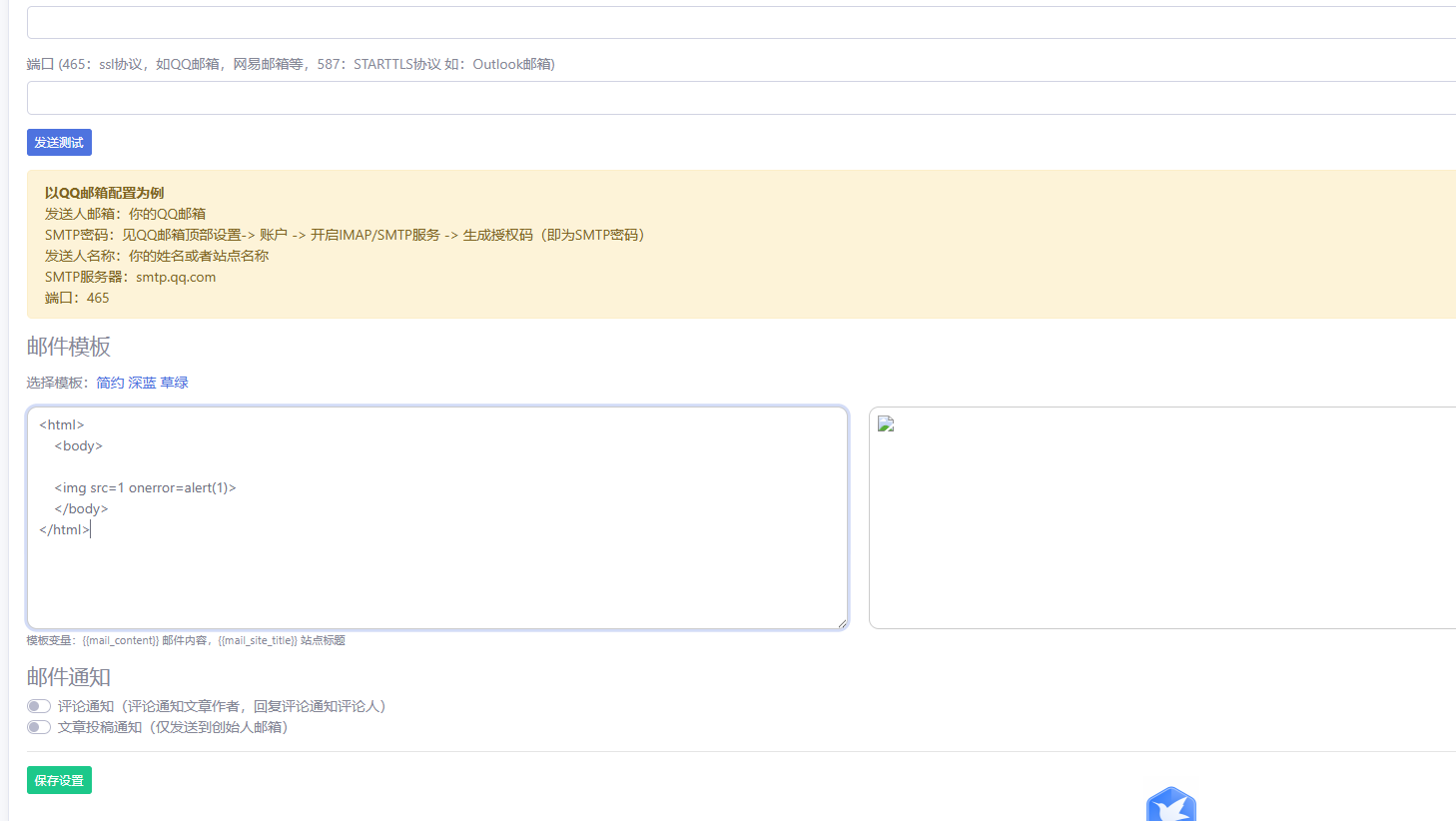
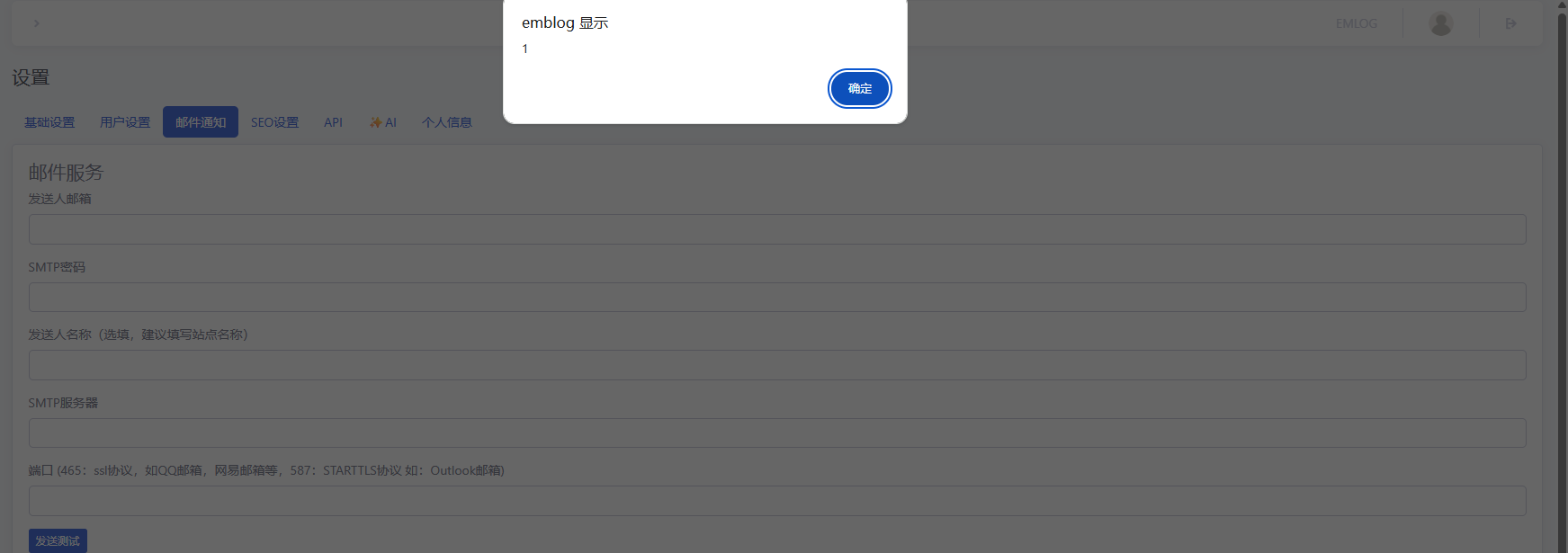
Subsequently, every time the email template configuration page is accessed, the XSS payload is automatically triggered:
Vulnerable Code Analysis
The vulnerability exists in the email template configuration component, which fails to properly sanitize user-supplied HTML input before storing it in the database and rendering it back to users. The application has several critical security issues:
- No input validation for HTML content in the email template field
- No sanitization of potentially dangerous HTML attributes and event handlers
- Absence of Content Security Policy (CSP) to restrict script execution
- Direct storage and rendering of user-supplied HTML without encoding
Impact
This vulnerability allows attackers with administrative access to:
- Execute arbitrary JavaScript code in the context of other administrators’ browsers
- Steal sensitive information such as session cookies and authentication tokens
- Perform unauthorized actions on behalf of victim administrators
- Potentially escalate to more severe attacks or system compromise
While this vulnerability requires administrative access to exploit, it can be used as part of a chain attack where a lower-privileged user gains administrative access and then leverages this vulnerability to maintain persistence or escalate privileges further.
Remediation
To fix this vulnerability, the application should:
- Implement proper HTML sanitization for the email template input
- Strip or encode potentially dangerous HTML attributes and event handlers
- Implement a Content Security Policy (CSP) to prevent execution of inline scripts
- Consider using a template system that automatically escapes HTML content
- Validate user input against a whitelist of allowed HTML tags and attributes
Timeline
- 2025-08-21: Vulnerability discovered
- 2025-08-21: Documentation and proof of concept created
- [Future Date]: Vulnerability reported to vendor
- [Future Date]: CVE assigned